According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) data, a mounting global challenge is being posed to individuals, families, and countries. The 2021 IDF report reveals that 10.5% of adults aged 20 to 79 are afflicted by diabetes. Referred to as the “silent killer,” diabetes can quietly develop without one’s awareness, with approximately half of the population being oblivious to its presence. The IDF predicts that by 2045, a 46% surge will occur, resulting in 1 in 8 adults (roughly 783 million people) grappling with diabetes. Along with the increase in diabetes, the blood glucose monitoring market is growing rapidly. People can use blood glucose monitoring to determine if they have diabetes or if they are at risk of developing the disease.
I. The Development Status of Blood Sugar Monitoring Market
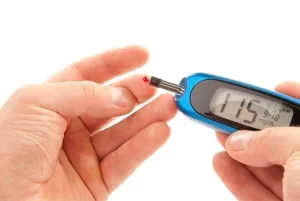
Blood sugar monitoring is an important aspect of diabetes management. With the rising prevalence of diabetes globally, the blood sugar monitoring market has experienced substantial expansion and innovation in recent times. According to Fortune Business Insight analysis, the global blood glucose monitoring market was valued at $15.80 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $32.99 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.9%. Several key factors are driving growth and progress in the blood sugar monitoring space.
1. Focus on developing CGM systems
Firstly, there is an increasing focus on developing continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems that can provide real-time glucose readings rather than just periodic snapshots. Major CGM manufacturers like Dexcom, Abbott, and Medtronic have released advanced CGM devices with features like longer sensor wear, reduced calibration requirements, and connectivity to smartphones. The convenience and actionable insights from CGM are leading to higher patient adherence and improved health outcomes.

2. Remote patient monitoring platforms can collect and analyze data
Secondly, mobile health apps and remote patient monitoring platforms are enabling better data aggregation and analysis, providing both patients and healthcare providers with meaningful patterns and trends. For example, Glooko’s diasend platform securely syncs data from over 95% of meters and CGMs to provide comprehensive glucose pattern recognition.
3. Development of non-invasive monitoring
Thirdly, non-invasive monitoring solutions are starting to emerge. Companies like PKvitality are working on continuous glucose wristbands that can track glucose without any skin pricks. Although still in the early stages, non-invasive tech may expand glucose monitoring access and frequency if the accuracy challenges can be overcome.
II. Challenges of Blood Sugar Monitoring And Their Solutions
Though blood sugar monitoring helps a lot for people with diabetes, there are several challenges that exist with current monitoring methods. Addressing these can improve the ease and effectiveness of blood glucose tracking.
1. Inaccuracy of single point-in-time measurements
Fingerstick meters provide just a snapshot of blood glucose at one moment. Levels fluctuate frequently, so these snapshots miss a lot of data. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices address this by providing a comprehensive view of trends and fluctuations. Though costly, increased CGM adoption improves insights.
2. User error
Improper handwashing, device calibration issues, and strip mishandling can provide incorrect readings. Enhanced user-friendly design, improved accuracy, and wireless connectivity in next-gen meters help minimize mistakes. Proper training and education on monitoring for patients also help.
3. Discomfort from fingersticks
For periodic monitoring via fingersticks, lancing and repeated finger wounds can be painful. Advances like alternate site testing, shallower lancets, and non-invasive tech like wrist-worn CGM reduce discomfort and increase testing adherence.
4. Cost barriers
High costs of advanced CGM sensors and readers limit access, especially in developing countries. Insurance coverage expansion and lower-cost generic devices could improve affordability. Non-invasive CGM tech currently in development may also potentially cut costs if accuracy can be achieved.
5. Data management challenges
Tracking, analyzing, and sharing glucose data with healthcare teams can be burdensome. Integrated mobile apps and cloud-based data platforms allow more seamless data capture, analytics, and provider access for better insights and treatment adjustments.
By leveraging technology progresses and overcoming limitations, blood sugar monitoring can become more convenient, insightful, and impactful. Continued innovation and patient education on existing tools is key to unlocking the full benefits of glucose data for diabetes management.
III. Blood Sugar Monitoring Market Share
According to Fortune Business Insight analysis, the global blood glucose monitoring market was valued at $15.80 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $32.99 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.9%. The market is being driven by the growing prevalence of diabetes and the increasing adoption of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices.
Diabetes affects over 400 million people worldwide, many of whom require regular blood glucose testing and monitoring. CGM devices, which allow real-time monitoring of blood sugar levels, are becoming more popular among both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes patients. The convenience and improved glycemic control offered by CGM are leading to wider usage.
North America currently dominates the global blood glucose monitoring market share. The region’s market size in 2022 is USD 6.92 billion. The large diabetic patient population and rapid penetration of advanced monitoring technologies have contributed to North America’s leading position.
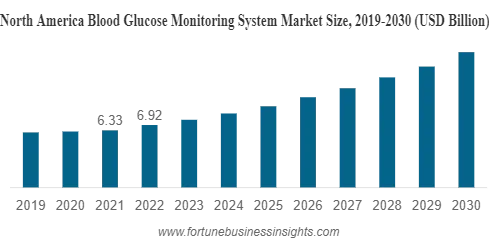
Europe held the second largest market share, followed by Asia Pacific. Driven by increased awareness, favorable reimbursement policies, and a large diabetic population, Europe follows North America in terms of market share. Whereas, Asia Pacific is expected to exhibit the fastest growth rate during the forecast period with increasing healthcare expenditure in countries such as China and India due to improving healthcare infrastructure.
According to the report, the key players in the blood sugar monitoring market include Roche, Abbott, Dexcom, Medtronic, and Senseonics. These companies have been investing in research and development in order to introduce innovative products that improve the accuracy and convenience of blood glucose monitoring.
For example, Abbott’s FreeStyle Libre continuous glucose monitoring system received FDA approval in 2017. This revolutionary product measures blood glucose levels without the use of a pointer. The introduction of such innovative products has fueled the growth of leading suppliers.
III. Trends in Blood Sugar Monitoring
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM devices stand out as a paramount breakthrough in glucose monitoring. In contrast to periodic fingerstick measurements, CGM offers a continuous stream of real-time glucose level data throughout the day and night. Some notable merits of CGM encompass:
- Enhanced comprehension of glucose trends and patterns.
- Capability to monitor the effects of food intake, physical activity, and medication.
- Customizable alerts and alarms for glucose levels that fall outside the target range.
- Elimination of the need for fingerstick tests in some of the newer “flash” CGM systems.
Prominent CGM manufacturers like Dexcom and Abbott are rapidly advancing their sensors and algorithms. Their efforts are focused on reducing device size, enhancing accuracy, prolonging longevity, and reducing costs. As a result, both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics are increasingly adopting and utilizing these technologies.
Connected Monitoring
Another noteworthy trend involves the direct connection of blood glucose meters with smartphones and tablets. Companies like OneDrop have introduced meters equipped with built-in Bluetooth technology that automatically syncs data to mobile apps. Alternatively, some devices allow manual data synchronization through wireless connections. This seamless integration makes it effortless to monitor, share, and analyze glucose data using digital platforms. Additionally, it enables remote monitoring by healthcare professionals and caregivers.
Analytic and Big Data
The substantial volume of data generated by CGM and connected meters is opening doors to advanced analytics. Companies are using insights from historical blood glucose data to provide personalized guidance and insights. For example, identifying patterns related to meals, exercise, and medications. Big data analytics will also facilitate improvements in alarm algorithms and artificial intelligence for glucose monitoring.
ABOUT MOKO MEDTECH
MOKO is an ISO9001 and ISO13485-certified full-service OEM manufacturer. Our factory covers an area of 12400㎡, including a clean workshop area of 2600㎡. In conjunction with our services and IoT industry experience, we offer our customers a highly integrated environment to move from prototype to production in dramatically compressed time frames. Our factory has a complete range of electronic component placement devices, soldering equipment, and specialized electronic assembly instrument that deliver productive and top-quality blood sugar monitoring device assembly.