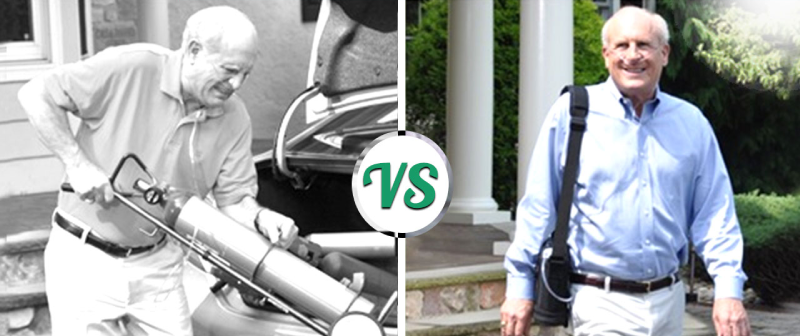
This text contains a comprehensive comparison between oxygen concentrator vs. oxygen tank from eight aspects. And, we also give some advice to different potential customers to choose right medical device for oxygen therapy.
Work Principle
Oxygen tanks are the most common way to offer medical-level oxygen to patients. Generally speaking, oxygen tanks are made of aluminum or steel. There are two types of oxygen tanks – one that holds compressed oxygen and one that holds oxygen in the form of liquid.
Oxygen in the tank is extracted from the air and compressed at a high pressure of two thousand and two hundred PSI. Thus, oxygen inside have to go through a regulator before outputting for patient inhalation.
To create liquid oxygen, gaseous oxygen is cooled to -297 degrees Fahrenheit, and then stored in vacuum insulated containers so as to keep the oxygen in a liquid state. The volume of one liter of liquid oxygen is equivalent to 860 liters of gaseous oxygen. In other words, liquid oxygen takes up much less storage space than oxygen in the form of gas. After exposed to room temperature, liquid oxygen are immediately changes to gas. Then, it is ready to consume by patients.
However, oxygen concentrators are very different from traditional oxygen tanks because they do not store oxygen. In common, air is composed of 21% oxygen, 78% nitrogen and 1% other gases. Oxygen concentrators receive air and filter out nitrogen to retain oxygen before it deliver oxygen through nozzles. Oxygen concentrators can provide about ninety-three percentage to ninety-seven percentage pure oxygen.
They deliver air in a continuous or pulse dose way. Continuous flow means a consistent amount of oxygen no matter how much breaths per minute the patient is taking. In contrast, pulse flow delivers oxygen with periodic fluctuation of output volume. Oxygen concentrators with pulse flow function can detect the user’s breathing and deliver oxygen according to their inhalation rhythm.
Portability

A, B, C, D, JD, E type oxygen tanks are portable. Besides, some of these tanks is configured a trolley. With the support of accessorial trolley, liquid oxygen can be used outdoors. Depending on capacity and oxygen consumption, many of these small portable oxygen tanks can provide oxygen for above ten hours.
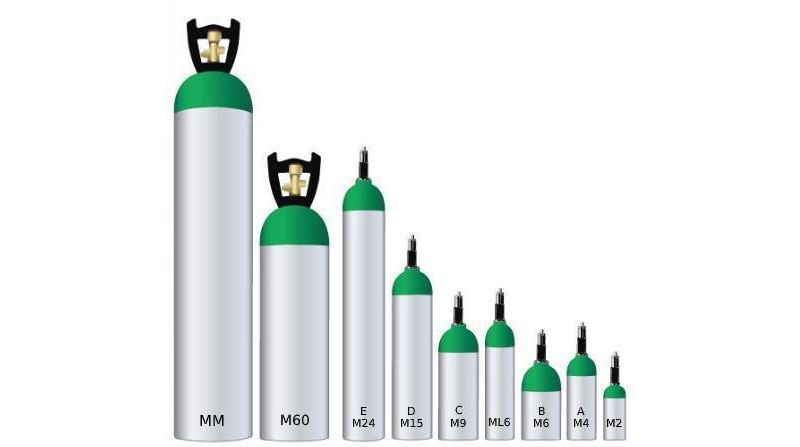
However, portable oxygen concentrators (POCs), as the name means, features higher portability than other types. They are powered by rechargeable batteries and concentrate oxygen on their own, so they can be taken anywhere with ease. In common, POC is equipped with a DC charger to fit cigarette lighter outlet in your car so as to make charging convenient. Last but not least, POC so small that it can be put in bag style suitcase.
Weight
Oxygen tanks differs in size and capacity. A common E-tank can fully deliver six hundred eighty liters of oxygen according to 2015 PSI. With this capacity, the tank can delivering oxygen at a flow rate of 2L/min for over 5 hours, with 8 pounds weight.
If you are need high oxygen flow, it is recommended to use H or M250 gas tanks. These large tanks weigh about one hundred and twenty pounds. In particular, the oxygen tanks, which are specially designed to contain cold liquid oxygen, takes up an significant part of the weight.
In comparison, portable oxygen concentrators are small in size and light in weight. The smallest portable one is Moko Mini Air, which only weighs three pounds. However, Moko Mini Air does not give in to light weight by cutting its effect. It can keep working for over four hours to meet the needs of patients with active lifestyles.
Another type of oxygen concentrator, home oxygen concentrator, is used at home and capable of bringing a continuous flow of oxygen above 10L/ min. Due to the application site and high air flow, this type are larger than portable oxygen concentrators, weighing about 30 pounds. However, they are still mobility, since they have wheels on the bottom or nice handle on the top of the machine.
Safety
Although both of these medical devices seems commonly safe, the risk of leaks should not be ignored. For example, a leakage of oxygen tanks results in pure oxygen filling the whole room. With such pure oxygen in the room, a little spark can be raised to a big fire.
In contrast, oxygen concentrators only collect and filter the surrounding air and then output the pure oxygen to your mouth and nose directly, so there’s lower risk of fire disaster.
Cost
At first glance, oxygen tanks aren’t expensive, costing only a hundred dollars. If you have used it for a long run, you may find that it is costly and inconvenience. Each time when you used up the air, you have to refill it.
Oxygen concentrators are expensive upfront, needing thousands to several thousand dollars at the initial buying. However, long-term cost in this machine are totally is good, because it doesn’t need frequent refilling and maintenance.
Last, don’ forget to consider the necessary cost of oxygen accessories no matter of oxygen tank or concentrator, such as a nasal cannula, oxygen tubing, and oxygen masks. If you want to save cost, we advise you to purchase them in bundles together so as to get a discount as well as organize and storage easily.
Clinical Effect
Ambulatory oxygen therapy is often provided to patients with lung disease to avoid short breath and improve quality of life. Lightweight portable oxygen concentrators becomes an additional choice except for traditional portable systems, such as oxygen tank.
However, their therapy effect on patients with lung disease has not been assessed. We find a study which is aimed to compare the clinical performance of a POC versus a oxygen tanks during 6-minute walk tests in patients with lung disease.
Methods: Ten patients with lung disease, which is caused by various aetiologies, were recruited. All of them can suffer from exertional oxygen desaturation (<90%) after 6-minute walk tests. Each participant takes part in two-day assessment:
Day 1 – Two 6-minute walk tests on room air
Day 2 – Two types testing models are designed. In one 6-minute walk tests, participants breathed oxygen via the portable oxygen concentrator. In the other 6-minute walk test, participant used oxygen tank (5L/minute).
Remark: This study keep two types oxygen devices weigh in same by adding additional weight to the portable oxygen concentrator .
Results: There was no significant difference in mean nadir oxygen saturation in Day 2 testing between using oxygen concentrators and using oxygen tank. (82.3% versus 80.3% respectively).
Most participants desaturated to below 80% during 6-minute walk tests, when using the oxygen tank (50%) and portable oxygen concentrator (20%). Both devices provided equivalent oxygenation at their rest time.
There was no significant difference in walking distances when using different devices .
Oxygen Concentrator Vs. Oxygen Tank: Five participants preferred portable oxygen concentrator, while only one preferred the oxygen tank.
Conclusion: The results suggest that portable oxygen concentrator had equivalent clinical effect to the oxygen tank during walking for patients with lung diseases and exertional desaturation.
Refills
Oxygen tanks need to be replenished or replaced from the supplier every week or two, depending on patients’ consumption. Besides, you have to stay at home when the doctor visits, and the long-run cost is not good for chronically ill man.
Home oxygen concentrator do not require reoxygenation. This is a major advantage since the user does not have to worry about replacing the tank if the oxygen is depleted. What it needs is power source, which is easy to get and costs few money. Moreover, concentrators benefits the patients who requiring continuous oxygen or high flow rates a lot, because it can provide infinite oxygen until it go bad.
Flight
What’ more, portable oxygen concentrators can be approved by FAA and TSA. In other words, you are allowed to bring approved oxygen concentrators to the flight. How to use it? All you need to do is carry enough batteries and fit under the seat or in the overhead bin, and you can enjoy a wonderful flight. However, oxygen tanks are not allowed to carry in the flight by the FAA.
Oxygen Concentrator Vs. Oxygen Tank: Five Advice for You
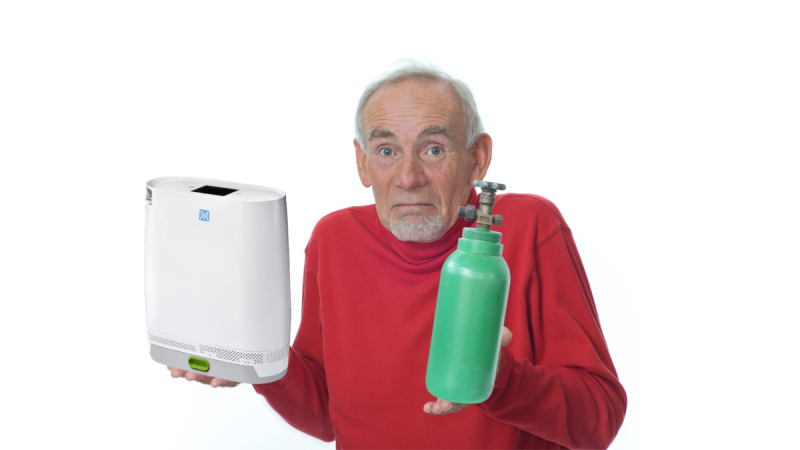

| Oxygen Concentrator Vs. Oxygen Tank | Oxygen Tank | Oxygen Concentrator |
| Pros | Work without the need of a power source Sounds so quiet during operating Lower upfront cost for short term | Versatility Portability Great long-term investment |
| Cons | Too Heavy and big to carry outdoor More expensive in the long term | Expensive for short term Noise Need power source |
Short-Periods User
If you need a short-term oxygen therapy, you will be prescribed a tank for home-use.
Sleep Apnea Syndrome
If you are confirmed getting sleep apnea syndrome, you will be prescribed a home oxygen concentrator machine. In fact, all of patients requiring sleeping oxygen therapy can be served well by oxygen concentrator, because it can give continues flow all the night without worrying about refilling oxygen.
User Required Flight
Only oxygen concentrator is allowed by FAA, while oxygen tank is banned. Because the liquid oxygen stored in tank is a kind of flammable and explosive items, it may cause an explosion in the high-altitude environment. In contrast, the oxygen concentrator doesn’t carry pure oxygen. It just concentrate and filter the air.
Long-term User
If you suffer from long-term lung disease, oxygen concentrator is your best choice as what was mentioned in above table of Oxygen Concentrator Vs. Oxygen Tank. From the perspective of cost, it can save lots of money spending in air refilling and maintenance. For safety, it is more safe to put it in your home than the oxygen tank.
Patient Requiring High Air Purity
According to United States Pharmacopeia (USP) standards, the oxygen purity of oxygen tanks or cylinders must not be less than 99%. Typically, compressed and liquid oxygen is stored at 99.5% purity.
Standard medical oxygen generator oxygen concentration is about 93%. There are 6% difference, which may be significant for some emergency state.
Takeaway
If you would like to purchase or customize a batch of advance oxygen concentrator, please feel free to contact us. If you want more about oxygen concentrator Vs. oxygen tank and tips about other medical devices, please keep close eyes to our channel.